Math 445 sample exam 1 with solutions
Problem 1. Write one line of Matlab code that assigns a 3-d column vector with
components 4,5,7 to variable x.
x = [4; 5; 7]
or
x = [4 5 7]'
Problem 2. Write one line of Matlab code that assigns a 3-d row vector with
components 4,5,7 to variable x.
x = [4 5 7]
Problem 3. (Note: We haven't done permutations yet so you're not required to know this material.) Write Matlab code that simulates the shuffling of a deck of cards by producing a random permutation of the integers 1 through 52.
randperm(52)
Problem 4. Write Matlab code that draws a unit circle, using the formulae  and
and  for 200 evenly spaced values of theta between 0 and 2pi. Label the
axes and make the circle red.
for 200 evenly spaced values of theta between 0 and 2pi. Label the
axes and make the circle red.
theta = linspace(0,2*pi, 200);
x = cos(theta);
y = sin(theta);
plot(x,y,'r')
xlabel('x');
ylabel('y');
or
theta = linspace(0,2*pi, 200);
plot(cos(theta), sin(theta), 'r')
xlabel('x');
ylabel('y');
Problem 5. Write a conditional expression that evaluates to 1 (true) if x and y
are equal or if either is zero.
Problem 6. Show how to solve the system of equations with three lines of Matlab code.
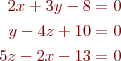
Note that the above equations need to be rearranged first
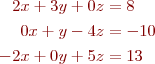
That can now be written as an Ax=b problem
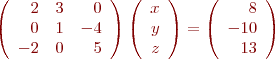
To solve in Matlab,
A = [2 3 0; 0 1 -4; -2 0 5]; b = [8; -10; 13]; x = A\b
Problem 7 Let A be an M x K matrix and B be an K x N matrix. Then the
product C = AB is an M x N matrix whose elements are given by
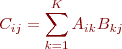
Write a Matlab function matmatmult that returns the product C of matrices
A and B. Use the above formula instead of Matlab's built-in matrix
multiplication!
function C = matmatmult(A,B);
% compute matrix-matrix product C = A*B
% find sizes of matrices
[M,K] = size(A);
[K,N] = size(B);
% allocate M x N matrix for answer C
C = zeros(M,N);
% compute each element C(i,j)...
for i=1:M
for j=1:N
% ...as sum from 1 to k of A(i,k)*B(k,j)
for k=1:K
C(i,j) = C(i,j) + A(i,k)*B(k,j);
end
end
end
end
Problem 8. Matrix multiplication C = AB is defined only for compatible matrices:
the number of columns of A must equal the number of rows of B. Write a short piece of
Matlab code that could be inserted in your matmatmult function that prints an error message
and returns a null (0 x 0) matrix if A and B are incompatible.
I'll provide the whole function with the inserted code
function C = matmatmult(A,B);
% compute matrix-matrix product C = A*B
% find sizes of matrices
[M,K1] = size(A);
[K2,N] = size(B);
% test that # cols of A == # rows of B
if K1 ~= K2
fprintf('matmatmult dimension mismatch: A has %d cols but B has %d rows\n', K1, K2);
% reset M,N to zero so that the function returns a 0 x 0 value for C
M = 0;
N = 0;
end
% allocate M x N matrix for answer C
C = zeros(M,N);
% compute each element C(i,j)...
for i=1:M
for j=1:N
% ...as sum from 1 to k of A(i,k)*B(k,j)
for k=1:K
C(i,j) = C(i,j) + A(i,k)*B(k,j);
end
end
end
end
