Table of Contents
Math 445 lecture 2: Vectors
topics
[] % creating vector vectors with square brackets () % accessing/assigning vector elements with parentheses ' % the transpose operator, apostrophe : % the colon operator, making range vectors + - % vector addition, subtraction .* ./ .^ % elementwise vector operations
Vectors in math
Vectors are hugely important in math, science, engineering. In math, a vector is a list of numbers. E.g. this is a 3-d vector
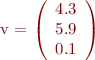
In math, the components or elements of a vector are written with subscripts. E.g. for the above vector

Creating vectors with explicit lists in square brackets
In Matlab, there's a distinction between row vector and column vectors. You can construct row vectors by listing elements between square brackets, with either spaces or commas between.
>> v = [4.3 5.9 0.1] % assign a row vector into variable v
v =
4.3000 5.9000 0.1000
To create a column vectors, put semicolons between the elements.
>> v = [4.3; 5.9; 0.1] % assign a col vector into variable v
v =
4.3000
5.9000
0.1000
Accessing elements with parentheses
In Matlab, you access the elements of a vector using parentheses. E.g. given the above vector v, you get the 2nd component of v this way
>> v(2)
ans =
5.9000
Note what happened there. We asked Matlab for the 2nd element of v. It returned the value 5.9 and assigned it to the default return variable ans. Alternatively, the following will assign or set the value of the second component of v to another number.
>> v(2) = 2.7
v =
4.3000
2.7000
0.1000
The transpose operator ' (apostrophe)
Note that last method. In Matlab, the apostrophe ' stands for the transpose.
The transpose operator turns a row vector into a column vector, and vice versa.
>> v = [4.3 5.9 0.1]
v =
4.3000 5.9000 0.1000
>> v'
ans =
4.3000
5.9000
0.1000
>> u = v'
u =
4.3000
5.9000
0.1000
>> w = u'
w =
4.3000 5.9000 0.1000
Constructing vectors with the colon operator :
The Matlab colon operator : is used in a number of ways. Here we'll see how it can be used to create vectors. The most straightforward of these is the syntax m:n, which creates a row vector of the integers from m to n. E.g.
>> 1:10
ans =
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
>> x = 4:7
x =
4 5 6 7
You can also specify a step or increment between the elements using the syntax m:step:n. For example, 5:2:17 will produce a vector of odd integers between 5 and 17.
>> x = 5:2:17
x =
5 7 9 11 13 15 17
Lastly, the colon operator works with nonintegers, too. E.g.
>> x = 0:0.1:0.7
x =
0 0.1000 0.2000 0.3000 0.4000 0.5000 0.6000 0.7000