Selected problems from Attaway 3rd edition, chapters 1 and 2.
Problem 1: Create the following vectors twice, once using linspace and once using the colon operator.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 2 7 12
Problem 2: Use the colon and transpose operators to create a column vector that has values -1 to 1 in steps of 0.2.
Problem 3: Given a vector v of arbitrary length, write an expression that evaluates to the odd-numbered elements of v. Test your expression on vectors v of both even and odd length.
Problem 4: Given a vector v of arbitrary length, write assignment statements that store the first half of v in a vector v1 and the second half in a vector v2. Make sure your assignment statements work for v of both even and odd length.
Problem 5: Create a 4 x 2 matrix of all zeros and store it in a variable. Then replace the second row of the matrix with a 3 and a 6.
Problem 6: Create a 3 x 5 matrix of random real numbers, and then delete the third row.
Problem 7: What are the values of the following expressions? Explain why.
'c' == 'd' - 1 && 2 < 4
'c' == 'd' - 1 || 2 < 4
xor('c' == 'd' - 1, 2 < 4)
10 > 5 > 2
Problem 8: The value of 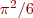 can be approximated by the sum of the series
can be approximated by the sum of the series

Write a one-line Matlab expression that evaluates the sum for the first  terms. Test it for a few values of
terms. Test it for a few values of  and compare to
and compare to 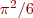 .
.
Problem 9: A vector v stores hours worked and hourly wages sequentially for a number of employees. For example
v = [33 10.5 40 18 20 7.5]
would specify three employees, the first working for 33 hours at $10.50/hr, the second 40 hours at $18/hr, etc. For an arbitrarily long v, write code that would separate v into an h vector of hours worked and a r vector of hourly wage rates, and then compute a w vector of wages owed to each employee. Do this as compactly as possible.
Problem 10: Evaluations at a university are scored 1-5, bad to good. However the evaluation forms mistakenly say that 1-5 is good to bad. So the computer program written to analyze evaluations must “reverse” all the evaluation scores. That is,
evals = [5 3 2 5 5 4 1 2]
should really be
evals = [1 3 4 1 1 2 5 4]
Write Matlab code that will reverse an arbitrary eval vector to the correct 1-5 scale.